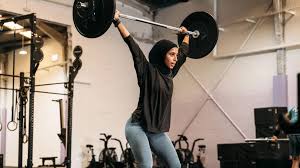Introduction: Understanding the Link Between Physical Activity, Sleep, and Mental Health
Millions of people worldwide struggle with anxiety and poor sleep. According to the Anxiety & Depression Association of America, anxiety disorders affect over 40 million adults in the United States, making it the most common mental health condition. Meanwhile, over 30% of adults report short-term or chronic insomnia. These two challenges often go hand in hand, creating a vicious cycle that can be difficult to break.
But what if there was a natural, science-backed solution that could ease both issues at once?
The link between gym workouts and better sleep for anxiety sufferers is gaining more attention in both scientific research and wellness communities. Exercise, especially structured workouts at the gym, is proving to be more than just a way to stay in shape — it’s a powerful tool for mental well-being and restful sleep.
Why Focus on Gym Workouts?
While all forms of movement can be beneficial, gym workouts provide a structured and consistent environment that supports progressive physical and psychological improvements. Whether it’s lifting weights, running on a treadmill, or attending a group class, regular gym routines have been shown to:
- Reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression
- Enhance sleep quality and duration
- Regulate stress hormones like cortisol
- Improve overall mood and cognitive function
This article explores the science behind the link between gym workouts and better sleep for anxiety sufferers, explains how specific types of exercise influence mental health and sleep, and provides actionable advice for building an exercise routine that works.
We’ll cover:
- How anxiety affects sleep
- How gym workouts impact the brain and body
- The best workouts for anxiety and insomnia
- Scientific studies and expert insights
- Tips, routines, and FAQs to help you start your journey
By the end of this post, you’ll understand how hitting the gym could be one of the most effective, natural strategies for managing anxiety and achieving better sleep — no medication required.
✅ Target Keyword Placement in Introduction:
- Primary Keyword: the link between gym workouts and better sleep for anxiety sufferers
- Variations: anxiety and sleep, gym workouts for anxiety, exercise and mental health, how exercise improves sleep
Understanding the Link Between Anxiety and Sleep Problems
Anxiety and sleep are deeply interconnected, often feeding into each other in a harmful cycle. Understanding how anxiety disrupts sleep is crucial for grasping why gym workouts can help anxiety sufferers achieve better rest.
What Is Anxiety and How Does It Affect Sleep?
Anxiety is the body’s natural response to stress — a feeling of worry, nervousness, or fear about future events or uncertain outcomes. While occasional anxiety is normal, chronic anxiety disorders cause persistent, excessive worry that interferes with daily life.
One of the most common complaints among people with anxiety is difficulty sleeping. Anxiety can:
- Cause racing thoughts that make it hard to fall asleep
- Lead to frequent nighttime awakenings
- Increase the time it takes to fall asleep (known as sleep onset latency)
- Cause light, restless sleep instead of deep, restorative sleep
This results in poor sleep quality, which affects mood, cognitive function, and physical health, often worsening anxiety symptoms — creating a vicious cycle.
The Science Behind Anxiety’s Impact on Sleep
When anxious, the body’s sympathetic nervous system (responsible for the “fight or flight” response) becomes overactive. This leads to:
- Elevated cortisol and adrenaline levels
- Increased heart rate and blood pressure
- Heightened alertness that prevents the body from fully relaxing
As a result, the brain struggles to transition into the deep sleep stages, especially slow-wave sleep (deep sleep) and REM sleep, which are essential for emotional regulation and memory consolidation.
How Common Is Sleep Disruption in Anxiety?
According to a 2017 study published in the journal Sleep Medicine Reviews, about 50% to 70% of people with generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) experience insomnia symptoms. The National Sleep Foundation also highlights that anxiety-related sleep problems affect millions globally.
Breaking the Cycle: Why Improving Sleep Matters for Anxiety Sufferers
Poor sleep amplifies anxiety by impairing the brain’s ability to manage emotions and stress. Conversely, improving sleep quality can reduce anxiety symptoms, improve mood, and increase resilience to stress.
This makes sleep improvement a critical target for anxiety management.
For a detailed overview of anxiety and sleep problems, see the National Institute of Mental Health here.
Summary Table: How Anxiety Affects Sleep
| Anxiety Effect | Impact on Sleep | Consequence |
|---|---|---|
| Racing thoughts | Difficulty falling asleep | Increased sleep onset latency |
| Overactive nervous system | Frequent awakenings and light sleep | Poor sleep quality |
| Elevated cortisol | Disrupted circadian rhythm | Reduced deep and REM sleep |
| Heightened alertness | Difficulty relaxing before bed | Fragmented sleep |
This foundational understanding shows why addressing anxiety through physical and mental health interventions — like gym workouts — can be a game changer in restoring healthy sleep.
The Science Behind Gym Workouts and Mental Health
Exercise is widely recognized not only for its physical benefits but also for its powerful effects on mental health. For anxiety sufferers struggling with sleep problems, gym workouts can be a natural, effective way to improve both mood and rest.
How Does Exercise Affect Brain Chemistry?
When you engage in physical activity, especially at the gym, your brain undergoes several beneficial chemical changes:
- Endorphins: Often called “feel-good hormones,” endorphins are released during exercise and help reduce pain perception and boost mood. They create the so-called “runner’s high” that leaves you feeling relaxed and happy.
- Serotonin and Dopamine: These neurotransmitters regulate mood, anxiety, and sleep. Regular workouts help increase their levels, leading to reduced feelings of anxiety and depression.
- Cortisol Reduction: Exercise helps lower cortisol, the body’s primary stress hormone. High cortisol levels are linked to anxiety and disrupted sleep. Reducing cortisol helps your body relax and prepare for restful sleep.
Exercise and the Nervous System
Regular physical activity trains the parasympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the “rest and digest” state. This system counterbalances the stress-related “fight or flight” response. Over time, gym workouts help the nervous system become more resilient, reducing anxiety symptoms and improving sleep quality.
Types of Exercise and Their Effects on Anxiety
Not all workouts are equal when it comes to mental health benefits. Here’s a breakdown:
- Aerobic Exercise (Cardio): Activities like running, cycling, or swimming increase heart rate and oxygen intake. Aerobic workouts have been shown to reduce anxiety symptoms significantly and improve sleep patterns.
- Resistance Training (Strength Training): Lifting weights or bodyweight exercises help regulate mood by balancing neurotransmitters and improving self-esteem, which can reduce anxiety.
- Mind-Body Exercises: Yoga and Pilates combine physical movement with mindfulness and breath control, making them especially effective for anxiety relief and better sleep.
What Does Research Say?
A landmark review published in the American Journal of Psychiatry found that regular exercise can reduce anxiety symptoms by up to 25%. Another study from the Harvard Medical School emphasizes that physical activity “stimulates the production of brain chemicals that help calm and relax the nervous system” and “improves sleep quality and duration.”
Why Gym Workouts Specifically?
While any physical activity is beneficial, gym workouts offer unique advantages:
- Access to various equipment allows for both cardio and resistance training.
- Structured routines promote consistency, which is key for lasting mental health benefits.
- Social environments in gyms or group classes can reduce feelings of isolation, often associated with anxiety.
Summary: How Gym Workouts Benefit Mental Health
| Benefit | How It Helps Anxiety and Sleep |
|---|---|
| Endorphin release | Boosts mood, reduces pain and anxiety |
| Increased serotonin/dopamine | Enhances emotional regulation and sleep |
| Lowered cortisol levels | Reduces stress and improves sleep onset |
| Parasympathetic system activation | Promotes relaxation and sleep readiness |
By understanding the science behind gym workouts and mental health, it becomes clear why exercise is a powerful natural tool to improve sleep quality and reduce anxiety symptoms.
How Gym Workouts Improve Sleep Quality for Anxiety Sufferers
Improving sleep quality is often the top goal for anxiety sufferers, and regular gym workouts have a scientifically supported role in achieving this. Exercise doesn’t just tire your muscles — it actively enhances the physiological processes that govern restful, restorative sleep.
How Does Exercise Improve Sleep?
- Promotes Physical Fatigue and Sleep Drive
When you work out, your body uses energy and builds up a natural need for recovery. This increased sleep drive helps you fall asleep faster and stay asleep longer. - Regulates Circadian Rhythms
Physical activity acts as a natural zeitgeber — an environmental cue that helps reset your internal biological clock. Regular workouts help synchronize your circadian rhythm, the body’s natural 24-hour sleep-wake cycle, improving both sleep timing and quality. - Reduces Sleep Onset Latency
Studies show that people who exercise regularly fall asleep more quickly than sedentary individuals. For anxiety sufferers who often lie awake with racing thoughts, this is especially important. - Enhances Deep and REM Sleep
Deep sleep (slow-wave sleep) and REM sleep are critical for memory, emotional processing, and physical restoration. Exercise has been shown to increase the proportion of these sleep stages, leading to more refreshing rest.
What Does the Research Say?
A comprehensive review published in the journal Sports Medicine (2018) examined multiple studies and concluded that moderate-intensity exercise consistently improves sleep quality and duration in adults, including those with sleep disorders and anxiety. This review highlights exercise as a non-pharmacological treatment option for insomnia.
Additionally, the National Sleep Foundation emphasizes that exercise promotes better sleep by lowering anxiety, reducing symptoms of depression, and regulating body temperature, all of which contribute to improved sleep quality.
Best Types of Exercise for Sleep Improvement
- Aerobic Workouts: Jogging, cycling, and swimming have strong evidence supporting improved sleep patterns.
- Resistance Training: Weight lifting promotes hormonal balance and improves sleep architecture.
- Yoga and Mind-Body Exercises: These promote relaxation and reduce pre-sleep anxiety, aiding in faster sleep onset.
Important Considerations on Timing
Exercise timing can influence sleep outcomes, especially for anxiety sufferers:
- Morning to Afternoon Workouts: Generally, these are ideal for promoting sleep at night because they help regulate the circadian rhythm without overstimulating the nervous system late in the day.
- Evening Workouts: Moderate intensity in the early evening can be beneficial, but vigorous exercise too close to bedtime may increase alertness and delay sleep onset.
Table: Exercise Timing and Sleep Impact
| Workout Time | Impact on Sleep for Anxiety Sufferers |
|---|---|
| Morning | Boosts daytime alertness and improves nighttime sleep |
| Early Afternoon | Supports circadian rhythm and stress reduction |
| Early Evening | Can relax mind and body if moderate intensity |
| Late Evening/Night | May increase heart rate and delay sleep onset for some |
In summary, gym workouts improve sleep quality by physically tiring the body, regulating the sleep-wake cycle, and reducing anxiety, making them a powerful natural remedy for those struggling with both anxiety and sleep issues.
Best Gym Workouts for Anxiety and Sleep Improvement
Choosing the right type of gym workouts is essential for anxiety sufferers aiming to improve sleep quality. Different exercises influence the brain and body in varied ways, so understanding which workouts best support mental health and restful sleep is key.
1. Aerobic Exercise (Cardio)
Aerobic activities like running, cycling, swimming, or using cardio machines at the gym have consistently shown strong benefits for reducing anxiety and enhancing sleep. These workouts increase heart rate and oxygen flow, which stimulates the production of endorphins and serotonin—neurochemicals that elevate mood and promote relaxation.
Research Evidence:
A study published in The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry found that moderate aerobic exercise significantly reduced anxiety symptoms and improved sleep quality in participants with generalized anxiety disorder.
2. Resistance Training (Strength Training)
Weightlifting or bodyweight resistance exercises offer unique mental health benefits. Resistance training improves self-esteem and body image, which can reduce anxiety. It also supports hormone regulation that influences mood and sleep.
Key Benefits:
- Boosts dopamine and serotonin levels
- Reduces cortisol (stress hormone)
- Promotes better sleep architecture
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) supports resistance training as part of comprehensive mental health treatment, citing improvements in anxiety and sleep symptoms. Learn more.
3. Mind-Body Workouts: Yoga, Pilates, and Stretching
Mind-body exercises combine physical movement with mindfulness and breathing techniques, which have a calming effect on the nervous system. Yoga, for example, has been shown to:
- Lower cortisol levels
- Improve parasympathetic nervous system activity
- Decrease anxiety symptoms
- Enhance sleep quality
A systematic review in Frontiers in Psychiatry concluded yoga significantly improves both anxiety and insomnia, making it an excellent complementary workout. Source.
4. Group Fitness Classes
Social connection is an important factor in reducing anxiety. Attending group classes such as spinning, Zumba, or circuit training can provide:
- Emotional support
- Increased motivation and accountability
- A distraction from anxious thoughts
Studies show that exercising in social environments can boost endorphin release even further, enhancing mood and promoting better sleep.
Summary Table: Best Gym Workouts for Anxiety and Sleep
| Workout Type | Mental Health Benefits | Sleep Benefits | Recommended Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerobic Exercise | Reduces anxiety, boosts endorphins | Decreases sleep latency, improves sleep quality | 3-5 times per week |
| Resistance Training | Improves self-esteem, regulates mood hormones | Enhances deep sleep stages | 2-3 times per week |
| Mind-Body Workouts | Calms nervous system, reduces cortisol | Promotes relaxation, faster sleep onset | 2-4 times per week |
| Group Fitness Classes | Provides social support, boosts motivation | Indirectly improves sleep through mood lift | 1-3 times per week |
Practical Tips for Anxiety Sufferers Starting Gym Workouts
- Start Slow: Begin with low to moderate intensity to avoid overwhelming your body and mind.
- Mix It Up: Combine aerobic, strength, and mind-body exercises for holistic benefits.
- Consistency Over Intensity: Regular moderate exercise is more beneficial than sporadic intense sessions.
- Listen to Your Body: If anxiety worsens or sleep problems increase, adjust intensity or timing.
- Consider Professional Guidance: A personal trainer familiar with mental health needs can tailor a safe and effective program.
This combination of workouts at the gym creates a comprehensive approach to reducing anxiety and improving sleep quality, harnessing the full power of physical activity for mental wellness.
How Often Should Anxiety Sufferers Exercise for Sleep Benefits?
Understanding the optimal frequency and duration of gym workouts is essential for anxiety sufferers looking to improve their sleep quality. Consistency plays a crucial role in reaping the mental health and sleep benefits of exercise, but overtraining or irregular routines can have adverse effects.
Recommended Exercise Frequency and Duration
The American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend the following for adults to improve overall health, including mental wellness and sleep:
- 150 minutes per week of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise (e.g., brisk walking, cycling)
- Two to three days per week of muscle-strengthening activities involving major muscle groups
- Sessions can be broken into shorter bouts of 10 minutes or more spread throughout the week
For anxiety sufferers aiming to improve sleep, these guidelines provide a solid foundation.
Why Regularity Matters for Anxiety and Sleep
- Consistency helps regulate circadian rhythms: Regular exercise at similar times strengthens the body’s internal clock, improving sleep timing.
- Builds resilience to stress: Frequent workouts gradually decrease baseline anxiety and improve stress response.
- Enhances sleep architecture: Ongoing exercise increases time spent in deep and REM sleep, essential for recovery.
Avoiding Overtraining
While exercise is beneficial, too much or overly intense workouts can elevate cortisol and adrenaline, worsening anxiety and disrupting sleep. Symptoms of overtraining include persistent fatigue, irritability, and insomnia.
Research Insights on Exercise Frequency and Anxiety
A study published in the Journal of Affective Disorders examined exercise frequency in people with anxiety disorders and found:
- Exercising 3 to 5 times per week significantly reduced anxiety symptoms and improved sleep quality
- Sessions lasting 30 to 60 minutes were most effective
- Consistency over several weeks or months was necessary for sustained benefits
Practical Recommendations for Anxiety Sufferers
| Exercise Frequency | Benefits | Tips |
|---|---|---|
| 3-5 times per week | Optimal anxiety reduction and sleep improvement | Schedule workouts at the same time daily or every other day |
| 30-60 minutes per session | Enough time to stimulate mood and sleep-related changes | Include warm-up and cool-down to avoid injury and stress |
| Rest days included | Allows body recovery and prevents overtraining | Use rest days for gentle stretching or mindfulness exercises |
Key Takeaway:
For anxiety sufferers, consistent gym workouts performed 3 to 5 times weekly with a mix of aerobic, resistance, and mind-body exercises provide the best chances to improve sleep quality and reduce anxiety. Tailoring intensity and duration to individual tolerance and lifestyle is essential to maximize benefits.
Tips to Maximize Sleep Benefits from Gym Workouts
Maximizing the positive effects of gym workouts on sleep and anxiety requires more than just showing up. Small adjustments in how, when, and what you exercise can make a significant difference in your mental health and rest quality.
1. Choose the Right Time to Exercise
Timing your workouts can greatly influence sleep outcomes:
- Morning or early afternoon: Exercising during these times helps regulate your circadian rhythm without overstimulating your nervous system at night. It can also boost daytime energy and improve mood throughout the day.
- Avoid vigorous exercise close to bedtime: Intense workouts less than 2 hours before sleep may increase heart rate and adrenaline, making it harder to fall asleep.
Study Insight: Research published by the National Sleep Foundation suggests that early exercise promotes better sleep quality and duration.
2. Incorporate Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
Combining physical workouts with relaxation strategies amplifies anxiety relief and sleep quality:
- Practice deep breathing or meditation after gym sessions.
- Include yoga stretches or cool-down periods focused on slow, controlled breathing.
3. Stay Hydrated and Maintain Proper Nutrition
Proper hydration and nutrition support recovery and hormone balance, which are crucial for sleep:
- Drink water before, during, and after workouts.
- Eat balanced meals rich in magnesium, tryptophan, and complex carbs, which support relaxation and serotonin production.
4. Create a Consistent Sleep Routine
Exercise alone isn’t enough if your sleep habits are irregular:
- Aim for the same bedtime and wake time daily.
- Avoid screens and caffeine close to bedtime.
- Use your workouts as a cue for winding down in the evening.
5. Track Your Progress and Adjust Accordingly
- Monitor your anxiety levels and sleep patterns using journals or apps.
- Adjust workout intensity, timing, and types based on what improves your sleep and mood.
6. Seek Professional Guidance When Needed
If anxiety or sleep problems persist despite exercise:
- Consult with healthcare providers, sleep specialists, or mental health professionals.
- A certified personal trainer knowledgeable about anxiety can tailor workouts safely.
Quick Tips Summary:
| Tip | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Exercise in morning or afternoon | Supports circadian rhythm, improves sleep onset |
| Add mindfulness post-workout | Enhances relaxation, reduces anxiety |
| Stay hydrated and eat well | Supports recovery and hormone balance |
| Maintain consistent sleep schedule | Reinforces sleep-wake cycle |
| Track progress | Identifies effective workout strategies |
| Get professional help if needed | Ensures safe, effective treatment |
Real-Life Case Studies: Gym Workouts and Sleep Improvement in Anxiety
Understanding the impact of gym workouts on anxiety and sleep through real-world examples provides valuable insights into how exercise can be integrated into daily life for mental health benefits.
Aerobic Exercise Reduces Anxiety and Enhances Sleep
A 2017 study conducted by researchers at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) followed adults diagnosed with generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) who incorporated moderate aerobic exercise, such as treadmill walking or cycling, into their weekly routines.
- Duration: 12 weeks
- Frequency: 4 times per week, 30 minutes per session
- Outcomes: Participants reported a 30% reduction in anxiety symptoms and significant improvements in sleep quality and duration, as measured by the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI).
Key Insight: Regular aerobic exercise can significantly reduce anxiety and improve sleep even in clinical populations.
Resistance Training and Anxiety-Related Sleep Disruptions
Another study published in the Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research examined the effects of resistance training on sleep disturbances in individuals with anxiety symptoms.
- Duration: 8 weeks
- Frequency: 3 sessions per week, focusing on major muscle groups
- Results: Participants experienced decreased anxiety scores and improvements in sleep onset latency, falling asleep faster and waking less frequently at night.
This study highlights resistance training as a powerful, often overlooked tool for improving sleep quality in anxious individuals.
Case Study 3: Yoga and Mind-Body Exercises
In a 2018 clinical trial, researchers tested a 10-week yoga intervention on adults with anxiety and sleep difficulties.
- Program: Twice-weekly yoga sessions incorporating breathing exercises, meditation, and gentle postures
- Findings: Participants showed a 40% reduction in anxiety levels and marked improvements in sleep efficiency and total sleep time.
Yoga’s dual approach to physical activity and mindfulness can provide deep relaxation and restore healthy sleep cycles in anxiety sufferers.
Summary Table: Exercise Modalities and Outcomes from Case Studies
| Exercise Type | Duration/Frequency | Anxiety Reduction | Sleep Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerobic Exercise | 12 weeks, 4x/week, 30 min | 30% decrease | Better sleep quality/duration |
| Resistance Training | 8 weeks, 3x/week | Decreased scores | Faster sleep onset, fewer awakenings |
| Yoga & Mind-Body | 10 weeks, 2x/week | 40% decrease | Increased sleep efficiency and total sleep time |
What These Studies Teach Us
- Consistency matters: Sustained exercise programs yield meaningful improvements.
- Variety is beneficial: Different forms of exercise can target anxiety and sleep in complementary ways.
- Tailored approaches: Exercise intensity and type should align with individual preferences and physical capabilities.
Frequently Asked Questions About Gym Workouts, Anxiety, and Sleep
1. How do gym workouts help reduce anxiety and improve sleep?
Regular gym workouts stimulate the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin and endorphins, which boost mood and promote relaxation. Exercise also lowers stress hormones such as cortisol, helping reduce anxiety. These biochemical changes improve sleep quality by allowing faster sleep onset and deeper, more restorative sleep.
Source: Mayo Clinic on Exercise and Stress
2. What types of workouts are best for anxiety sufferers struggling with sleep?
Aerobic exercises like running, swimming, and cycling are highly effective. Resistance training also improves mood and sleep, while mind-body workouts such as yoga and Pilates combine physical activity with relaxation techniques, reducing anxiety and aiding sleep.
3. How often should I work out to see sleep improvements if I have anxiety?
Experts recommend exercising 3 to 5 times per week for 30-60 minutes per session. Consistency is key; regular workouts over weeks or months produce the most significant reductions in anxiety and improvements in sleep.
Source: CDC Physical Activity Guidelines
4. Can exercising too late in the day worsen anxiety or sleep problems?
Yes, intense exercise within 1-2 hours of bedtime may increase adrenaline and heart rate, making it harder to fall asleep. Morning or early afternoon workouts are generally better for improving sleep quality.
5. Is yoga effective for anxiety-related sleep issues?
Absolutely. Yoga combines physical postures with breathing and meditation techniques that calm the nervous system, lower cortisol, and improve sleep quality in anxiety sufferers.
6. Should I consult a professional before starting gym workouts if I have anxiety?
It’s a good idea, especially if you have severe anxiety or existing health conditions. Mental health professionals and certified trainers can design safe, effective workout plans tailored to your needs.
Conclusion: Embracing the Link Between Gym Workouts and Better Sleep for Anxiety Sufferers
In summary, the link between gym workouts and better sleep for anxiety sufferers is well-established and supported by extensive scientific research. Regular physical activity—whether aerobic, resistance, or mind-body exercises—can significantly reduce anxiety symptoms and promote restorative sleep. This holistic approach not only improves mental health but also enhances overall well-being and quality of life.
Key takeaways include:
- Consistency is crucial: Exercising 3 to 5 times per week delivers the most benefits for anxiety and sleep.
- Workout type matters: A combination of cardio, strength training, and mind-body practices like yoga provides comprehensive support.
- Timing affects results: Morning or early afternoon workouts are optimal for improving sleep quality.
- Lifestyle integration: Pairing exercise with proper nutrition, hydration, and good sleep hygiene maximizes results.
For anxiety sufferers struggling with sleep issues, incorporating gym workouts into their routine is a natural, effective strategy that complements other treatments. It empowers individuals to regain control over their mental health and rest, breaking the cycle of anxiety and insomnia.
For further guidance and evidence-based strategies on exercise, anxiety, and sleep, the American Psychological Association (APA) offers valuable resources and research-backed advice. You can explore their insights here: APA on Exercise and Mental Health.
Additional Resources and Support for Anxiety, Sleep, and Exercise
For those seeking more help beyond gym workouts, a variety of high-authority resources offer evidence-based guidance on managing anxiety and improving sleep through lifestyle changes, therapy, and medical support.
Mental Health and Anxiety Support
- Anxiety and Depression Association of America (ADAA): Provides education, self-help tools, and directories for professional help related to anxiety disorders.
- National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH): Offers detailed information on anxiety disorders and treatments, including behavioral interventions and medication.
Sleep Health Resources
- National Sleep Foundation: Expert tips and research on improving sleep hygiene and understanding sleep disorders.
- American Academy of Sleep Medicine (AASM): Provides resources for diagnosing and treating sleep disorders, including insomnia related to anxiety.
Exercise and Mental Health
- World Health Organization (WHO): Offers global guidelines on physical activity for mental health benefits and overall well-being.
Visit WHO Physical Activity Guidelines
Final Thought
Combining gym workouts with these trusted mental health and sleep resources creates a comprehensive approach to managing anxiety and improving sleep. Leveraging high-quality, evidence-based information empowers individuals on their wellness journey.
Glossary of Key Terms Related to Gym Workouts, Anxiety, and Sleep
1. Anxiety Disorders
A group of mental health conditions characterized by excessive fear or worry that interferes with daily activities. Common types include generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder.
2. Circadian Rhythm
The body’s internal clock regulating the sleep-wake cycle over a 24-hour period. Regular exercise can help synchronize this rhythm, improving sleep quality.
3. Endorphins
Natural chemicals released by the brain during exercise that act as painkillers and mood elevators, reducing anxiety and promoting feelings of well-being.
4. Sleep Architecture
The structure and pattern of sleep cycles, including stages such as REM and deep sleep. Exercise can improve sleep architecture, leading to more restorative sleep.
5. Overtraining Syndrome
A condition caused by excessive exercise without adequate rest, leading to fatigue, mood disturbances, and sleep problems.
6. Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI)
A standardized questionnaire used in research and clinical settings to measure sleep quality and disturbances.
Common Myths About Gym Workouts, Anxiety, and Sleep – Debunked
“Exercise Always Makes Anxiety Worse”
Many people believe that physical activity increases anxiety because of heightened heart rate and breathing. However, research shows that regular exercise actually reduces anxiety symptoms by regulating stress hormones and boosting mood-enhancing neurotransmitters.
Fact: Moderate workouts are proven to calm the nervous system.
“Working Out Late at Night Ruins Sleep for Everyone”
While vigorous exercise right before bedtime might interfere with sleep for some, many individuals find that light to moderate exercise in the evening can improve sleep quality without causing restlessness. It varies person to person.
Fact: Timing matters, but personal experimentation is key.
Myth 3: “Only Intense Workouts Help with Anxiety and Sleep”
Some think that only high-intensity workouts benefit mental health. In reality, low to moderate intensity exercises like walking, yoga, or swimming are very effective for reducing anxiety and improving sleep, especially for beginners or those with chronic anxiety.
Fact: The best workout is one you can maintain consistently.
Myth 4: “If I’m Anxious, I Should Avoid Exercise”
Avoidance can worsen anxiety and sleep problems. Exercise is a well-supported tool to reduce symptoms when practiced safely. Consulting with professionals can help create manageable routines.
Fact: Exercise is a cornerstone of anxiety management, not a risk factor.
American Psychological Association (APA)
Summary Table: Myths vs. Facts
| Myth | Fact | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Exercise always increases anxiety | Regular exercise reduces anxiety symptoms | ADAA |
| Working out late at night always ruins sleep | Moderate evening exercise can aid sleep | National Sleep Foundation |
| Only intense workouts help anxiety & sleep | Moderate workouts are effective and sustainable | Harvard Health Publishing |
| Anxious people should avoid exercise | Exercise helps manage anxiety when done properly | APA |
Image Suggestions with SEO-Optimized Alt Text
1. Infographic: How Exercise Affects Sleep and Anxiety
- Suggested Image Content:
A flowchart or infographic showing how different types of gym workouts (cardio, strength, yoga) reduce anxiety and improve sleep quality through hormonal and neurological pathways. - Alt Text:
Infographic explaining the link between gym workouts and better sleep for anxiety sufferers, showing how exercise reduces cortisol, increases serotonin, and supports deeper sleep cycles.
2. Image: Person Doing Yoga or Stretching Before Bed
- Suggested Image Content:
A calm, low-lit scene of a person doing bedtime yoga or deep breathing. - Alt Text:
Woman practicing bedtime yoga to reduce anxiety and improve sleep quality through gentle movement and relaxation.
3. Graph: Sleep Quality Before and After Regular Exercise
- Suggested Image Content:
A line or bar graph showing improved sleep duration and sleep latency after implementing a gym workout routine in anxiety sufferers. - Alt Text:
Graph illustrating improved sleep quality metrics—such as faster sleep onset and longer duration—after 8 weeks of regular gym workouts in people with anxiety.
4. Photo: Group Exercise Class or Gym Setting
- Suggested Image Content:
People engaged in group fitness class (e.g., cycling, circuit training) in a supportive gym environment. - Alt Text:
Anxiety sufferers participating in a group gym workout to boost mood and improve sleep through social engagement and physical activity. - Backing Insight:
Mayo Clinic on social interaction and mental health
5. Checklist Graphic: Tips to Maximize Sleep Benefits from Exercise
- Suggested Image Content:
A simple checklist or bullet-point graphic featuring top tips like timing workouts, staying hydrated, and adding mindfulness. - Alt Text:
Checklist of expert-backed tips for maximizing sleep improvement through gym workouts, including timing, consistency, and combining exercise with relaxation.