Understanding the Gym Goers Goal
For anyone stepping into a gym, understanding your gym goers goal is the first and most important step toward achieving meaningful results. A gym goal is more than just wanting to “look fit” or “lose weight”—it’s a clearly defined target that guides your workouts, nutrition, and lifestyle choices. Without a goal, progress becomes random, motivation dips, and results are often slower than desired.
Gym goals can take many forms, and each has its own strategies and requirements:
- Weight Loss Goals: Targeting fat reduction while maintaining lean muscle mass. Common among beginners or those looking to improve overall health.
- Muscle Gain / Hypertrophy Goals: Building muscle mass through resistance training, protein-rich diets, and progressive overload techniques.
- Strength and Performance Goals: Increasing raw strength, power, and endurance for better performance in sports or daily activities.
- Endurance and Cardio Goals: Improving stamina and cardiovascular health through activities like running, cycling, or HIIT (High-Intensity Interval Training).
- Flexibility and Mobility Goals: Enhancing range of motion, reducing injury risk, and supporting overall functional fitness with yoga, stretching, and mobility drills.
According to a study published in the NYT Health section, people who set specific gym goals are more likely to stick to their routines and see measurable improvements than those who exercise without defined objectives. This emphasizes the importance of clarity in goal setting—it’s not enough to “go to the gym more often.” You need to ask: what do I want to achieve, and how will I measure success?
Key Takeaways:
- A gym goal is your roadmap to fitness success.
- Goals should be specific, measurable, and realistic to keep motivation high.
- Understanding your type of goal (weight loss, strength, endurance, etc.) determines the best workout and nutrition strategies.
Pro Tip: Start by writing down your gym goal. Include what you want to achieve, the timeline, and why it matters to you. This simple step dramatically increases accountability and progress tracking.
How to Set Realistic and Achievable Gym Goals
Setting a gym goers goal is more than deciding to “get fit” or “build muscle.” The most successful gym-goers are those who set realistic, specific, and measurable goals that they can consistently work toward. Without a clear roadmap, even the most motivated individuals may lose direction or plateau quickly.
1. Use SMART Goals for Fitness Success
One of the most effective frameworks for goal-setting is SMART goals, which stands for:
- S – Specific: Clearly define what you want to achieve. For example, instead of “I want to get stronger,” say, “I want to increase my bench press from 100 lbs to 150 lbs in 12 weeks.”
- M – Measurable: Include quantifiable indicators to track progress. Use metrics like weight lifted, body fat percentage, or number of repetitions.
- A – Achievable: Set goals that challenge you but are realistic based on your current fitness level. Avoid overly ambitious targets that may lead to frustration or injury.
- R – Relevant: Ensure your goal aligns with your lifestyle, schedule, and long-term fitness vision. For example, a high-intensity training goal might not be relevant if you’re recovering from an injury.
- T – Time-bound: Assign a clear timeline. Deadlines create urgency and focus your efforts, whether it’s a 6-week challenge or a 12-month transformation plan.
Example of a SMART gym goal:
“I will perform a 3-day full-body strength training program, increase my squat from 80 kg to 100 kg, and reduce body fat from 22% to 18% within 12 weeks.”
2. Differentiate Between Short-Term and Long-Term Goals
Breaking down your fitness journey into short-term and long-term goals makes it easier to stay motivated:
- Short-Term Goals (4–6 weeks): Focus on immediate improvements like increasing reps, mastering proper form, or losing 2–3 kg.
- Long-Term Goals (3–12 months): Larger transformations such as significant muscle gain, endurance improvement, or weight loss targets.
Short-term wins give psychological boosts and reinforce habit-building, which is critical for reaching your long-term gym goers goal.
3. Common Goal-Setting Mistakes to Avoid
Even with the best intentions, many gym-goers stumble when setting goals. Avoid these pitfalls:
- Being too vague: “I want to get fit” is unclear and unmeasurable.
- Setting unrealistic expectations: Expecting a 20 kg weight loss in 4 weeks is unsafe and unsustainable.
- Ignoring recovery and lifestyle factors: Overtraining or neglecting sleep and nutrition can sabotage progress.
- Not tracking progress: Without consistent monitoring, it’s impossible to know if you’re improving.
4. Tools and Techniques to Track Progress
Tracking your fitness journey is essential for achieving your gym goers goal. Several tools and techniques can help:
- Fitness apps: MyFitnessPal, Fitbod, or Strong for tracking workouts and nutrition.
- Journals or notebooks: Write down sets, reps, and workout notes manually.
- Body metrics: Use scales, tape measures, or body fat calipers to monitor changes.
- Photos: Weekly progress photos help visualize subtle changes that numbers may miss.
Case Study: A 2022 NYT Health article highlighted a study showing that gym-goers who tracked their progress weekly were 40% more likely to meet their fitness goals compared to those who did not. This demonstrates that tracking isn’t just optional—it’s a crucial part of success.
5. Featured Snippet Opportunity – 5 Steps to Set a Gym Goal
- Define what you want to achieve (weight loss, strength, endurance, etc.)
- Make it SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound)
- Break it into short-term and long-term goals
- Track your progress consistently with apps or journals
- Adjust your plan if you hit plateaus or challenges
Key Takeaways:
- A well-defined gym goers goal provides clarity and direction.
- SMART goals and short-term/long-term planning increase motivation and consistency.
- Tracking progress is one of the most powerful predictors of success.
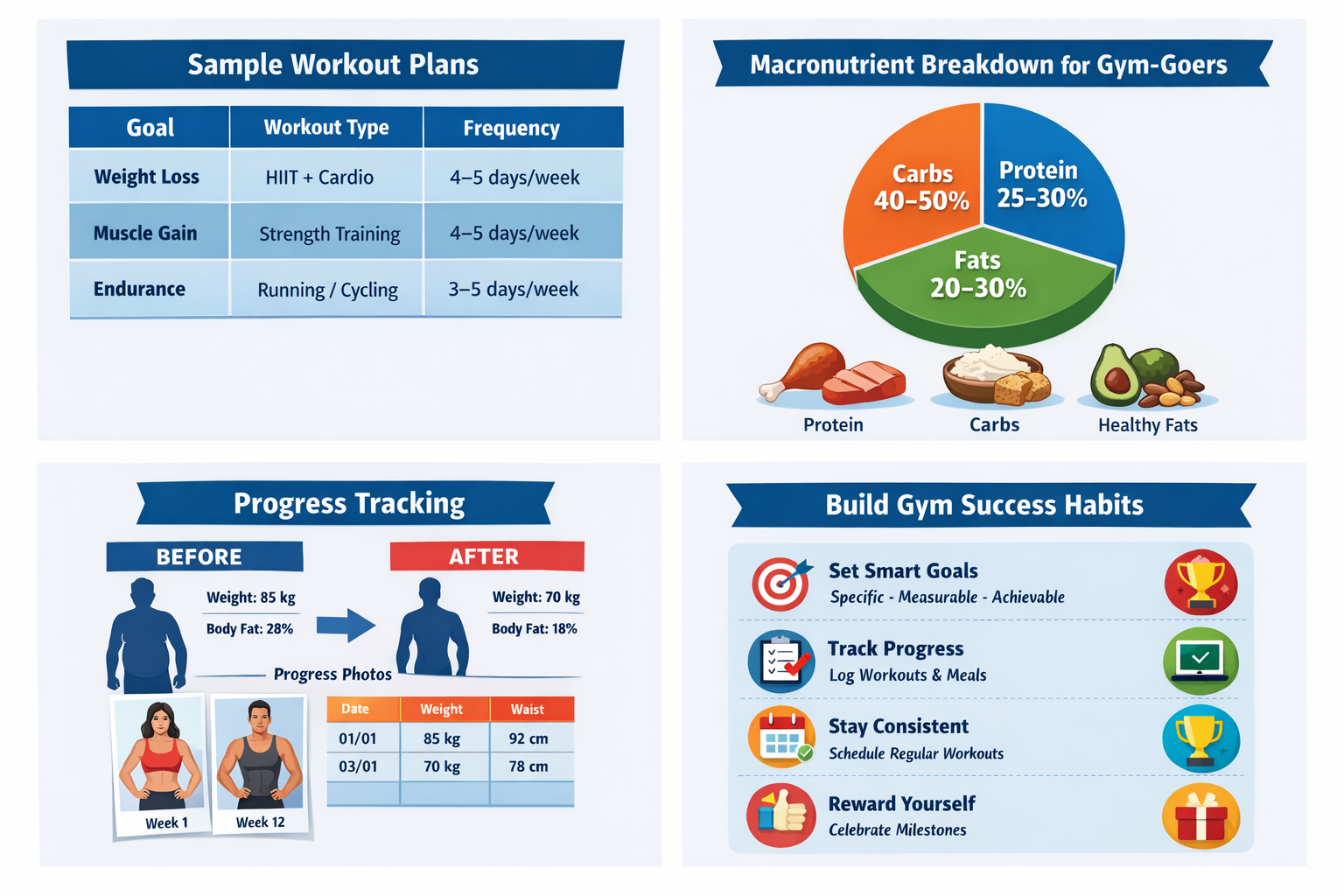
Workout Plans to Match Your Gym Goals
Achieving a gym goers goal requires more than just showing up at the gym—it demands a structured, goal-oriented workout plan. Different fitness goals require different approaches, and understanding which exercises align with your objective is crucial for success.
Workout Plans for Weight Loss
For those aiming to shed fat and slim down, the key is combining cardio, resistance training, and high-intensity exercises. Fat loss is best achieved through a mix of calorie-burning workouts and muscle-preserving strength training.
Recommended Exercises:
- High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT): Short bursts of intense activity followed by rest periods. For example, 30 seconds of sprinting followed by 60 seconds of walking, repeated for 15–20 minutes. HIIT has been shown to boost metabolism for hours after exercise.
- Cardio Workouts: Running, cycling, rowing, or swimming for 30–45 minutes, 3–5 times per week.
- Resistance Training: Full-body weightlifting 2–3 times per week to preserve lean muscle. Focus on compound movements like squats, deadlifts, and push-ups.
Sample Weekly Plan for Weight Loss:
| Day | Workout Type | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Monday | HIIT + Core | 30 min |
| Tuesday | Full-body Strength Training | 45 min |
| Wednesday | Cardio (Running or Cycling) | 40 min |
| Thursday | Rest or Light Yoga | 30 min |
| Friday | HIIT + Upper Body | 30 min |
| Saturday | Full-body Strength Training | 45 min |
| Sunday | Active Recovery (Walking/Stretching) | 30 min |
Pro Tip: Combining HIIT with strength training maximizes fat loss while keeping muscles toned.
Workout Plans for Muscle Gain
Building muscle, or hypertrophy, requires progressive overload, proper form, and sufficient recovery. Nutrition plays a critical role, but your training must target all major muscle groups efficiently.
Key Principles:
- Compound Exercises: Squats, bench presses, deadlifts, pull-ups—these recruit multiple muscles at once.
- Isolation Exercises: Bicep curls, tricep extensions, calf raises—for targeted growth.
- Progressive Overload: Gradually increase weight, reps, or sets to force muscles to adapt.
Sample Weekly Plan for Muscle Gain:
| Day | Focus Area | Exercises |
|---|---|---|
| Monday | Chest & Triceps | Bench Press, Incline Press, Dips, Tricep Pushdowns |
| Tuesday | Back & Biceps | Deadlift, Pull-Ups, Barbell Row, Bicep Curls |
| Wednesday | Rest | Recovery & Stretching |
| Thursday | Legs | Squats, Lunges, Leg Press, Calf Raises |
| Friday | Shoulders & Abs | Military Press, Lateral Raises, Plank, Russian Twists |
| Saturday | Full Body/Weak Points | Target weak muscle groups or functional training |
| Sunday | Rest | Active recovery (walking, yoga) |
Data Insight: Studies show that 3–5 days of structured resistance training per week, combined with proper protein intake, can increase muscle mass by 1–2 kg per month in beginners.
Workout Plans for Endurance and Performance
For gym-goers focused on improving stamina, athletic performance, or overall cardiovascular health, training emphasizes cardio, circuit training, and functional exercises.
Recommended Workouts:
- Cardio Conditioning: Long runs, rowing, cycling, or swimming for 45–60 minutes, 3–5 times per week.
- Circuit Training: Combine cardio and resistance exercises in circuits, e.g., 10 push-ups, 15 squats, 20 jumping jacks, repeat for 3–4 rounds.
- Functional Fitness: Exercises mimicking real-life movements like kettlebell swings, sled pushes, or battle ropes.
Pro Tip: Incorporating intervals and functional movements improves both cardiovascular fitness and muscular endurance, making workouts more efficient.
Workout Plans for Flexibility and Mobility
Flexibility and mobility are often overlooked, but they’re essential for injury prevention, recovery, and better overall performance.
Recommended Approaches:
- Yoga: Enhances flexibility, balance, and mental focus. Styles like Hatha or Vinyasa are beginner-friendly.
- Stretching Routines: Dynamic stretches pre-workout (leg swings, arm circles) and static stretches post-workout (hamstring stretch, shoulder stretch).
- Mobility Drills: Foam rolling, hip openers, ankle rotations, shoulder mobility exercises.
Tip: Dedicate 10–20 minutes daily to mobility work, especially if your gym goal involves lifting heavy or high-intensity training.
Key Takeaways:
- Your workout plan should align with your specific gym goers goal.
- Weight loss, muscle gain, endurance, and flexibility all require distinct strategies.
- Consistency and progression are the keys to achieving results efficiently.
- Combining multiple approaches (strength + cardio + mobility) often yields the best overall fitness outcomes.
Nutrition and Diet for Gym Goers Goal Success
Achieving your gym goers goal isn’t just about working out—it’s about fueling your body correctly. Nutrition directly affects performance, recovery, and results, making it as important as your exercise routine. The right balance of macronutrients, hydration, and timing can significantly accelerate progress toward your goals.
1. Importance of Nutrition in Achieving Gym Goals
Your body needs energy to perform, repair, and grow. Poor nutrition can limit gains, slow recovery, and increase fatigue. Research from NYT Health and Sports Science highlights that 80% of fitness results are influenced by diet, while only 20% come from workouts alone.
Proper nutrition ensures:
- Muscle repair and growth
- Adequate energy for high-performance workouts
- Efficient fat metabolism for weight loss goals
- Reduced risk of injury and overtraining
2. Understanding Macronutrients
Macronutrients are the building blocks of your diet. Balancing them according to your gym goal is crucial.
| Macronutrient | Role in Fitness | Recommended Intake for Gym-Goers |
|---|---|---|
| Protein | Muscle repair, growth, and satiety | 1.6–2.2g per kg of body weight/day |
| Carbohydrates | Primary energy source for workouts | 3–6g per kg/day for moderate training; higher for endurance athletes |
| Fats | Hormone regulation, energy, joint health | 20–30% of total calories from healthy fats |
Tip: For muscle gain, prioritize protein and carbs post-workout; for fat loss, maintain a slight calorie deficit but keep protein high to preserve lean mass.
3. Pre-Workout and Post-Workout Nutrition
Pre-Workout Nutrition: Fuel your body for optimal performance. Focus on:
- Easily digestible carbs for energy (e.g., oats, bananas, whole-grain toast)
- Moderate protein (e.g., Greek yogurt, whey protein)
- Hydration: 500 ml of water 30–60 minutes before training
Post-Workout Nutrition: Focus on recovery and muscle repair. Include:
- Protein-rich foods: chicken, fish, tofu, protein shakes
- Carbohydrates: rice, potatoes, fruits to replenish glycogen
- Healthy fats in moderation**: avocado, nuts, olive oil
Pro Tip: Consuming protein within 30–60 minutes post-workout enhances muscle protein synthesis, accelerating gains.
4. Supplements: What Works and What to Avoid
While whole foods are best, supplements can fill nutritional gaps:
Effective Supplements for Gym-Goers Goals:
- Whey Protein: Quick digestion, supports muscle growth
- Creatine Monohydrate: Improves strength, power, and performance
- Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs): May reduce muscle soreness during intense training
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Anti-inflammatory, supports joint health
Supplements to Be Cautious Of:
- Fat burners: often overhyped and unsafe if misused
- Pre-workouts with excessive caffeine: can cause jitteriness or disrupt sleep
NYT Health Tip: Focus on whole foods first, then supplement only where necessary.
5. Hydration for Optimal Performance
Water is essential for muscle function, energy production, and recovery. Even mild dehydration (2% body weight loss) can impair strength, endurance, and cognitive focus.
- Daily recommendation: ~2–3 liters of water for average adults; adjust for sweat loss
- During workouts: 150–350 ml every 15–20 minutes depending on intensity
- Electrolytes: For long endurance sessions, consider sodium, potassium, and magnesium replacement
6. Sample Nutrition Plan for Gym Goers Goal
Weight Loss: Moderate calorie deficit, high protein, balanced carbs and fats
| Meal | Food Example | Macronutrients |
|---|---|---|
| Breakfast | Oatmeal with whey protein & berries | 35g carbs, 25g protein, 8g fat |
| Snack | Greek yogurt + almonds | 10g carbs, 15g protein, 7g fat |
| Lunch | Grilled chicken, quinoa, veggies | 40g carbs, 30g protein, 10g fat |
| Pre-Workout | Banana + peanut butter | 30g carbs, 5g protein, 5g fat |
| Post-Workout | Protein shake + rice cake | 25g carbs, 25g protein, 2g fat |
| Dinner | Salmon + roasted veggies | 20g carbs, 30g protein, 12g fat |
Muscle Gain: Slight calorie surplus, high protein, moderate to high carbs
Tip: Adjust portions based on body weight, training intensity, and progress tracking.
Key Takeaways:
- Nutrition is as crucial as workouts for achieving a gym goers goal.
- Balance protein, carbs, and fats according to your objective.
- Timing meals around workouts boosts performance and recovery.
- Hydration and supplements can enhance results but are secondary to whole-food nutrition.
Motivation and Mindset for Gym Goers
Achieving a gym goers goal isn’t just a physical challenge—it’s a mental one. Motivation and mindset determine whether you stay consistent, push through plateaus, and make fitness a long-term habit. According to research cited in NYT Health, individuals who maintain a positive mindset and strong motivation are 50% more likely to achieve their fitness goals than those relying solely on willpower.
1. How Mindset Affects Goal Achievement
Your mental approach influences:
- Consistency: A motivated mindset keeps you showing up even on tough days.
- Effort and intensity: Positive thinking increases workout performance and reduces perceived exertion.
- Resilience: Helps you recover from setbacks like missed sessions, plateaus, or injuries.
Mindset Strategies:
- Growth Mindset: Believe that your abilities can improve with effort and time. For example, instead of thinking “I’m not strong enough for this weight,” say, “I’ll build strength gradually.”
- Process Over Outcome: Focus on daily actions like completing workouts and eating well rather than obsessing over the scale or mirror.
- Self-Compassion: Accept minor setbacks as part of the journey rather than giving up entirely.
2. Overcoming Gym Motivation Slumps
Even the most dedicated gym-goers face motivational challenges. Common causes include:
- Fatigue or burnout from overtraining
- Boredom from repetitive routines
- Unrealistic expectations leading to frustration
Practical Tips to Stay Motivated:
- Set micro-goals: Small, achievable targets give frequent wins (e.g., increase squat weight by 2 kg this week).
- Change your routine: Switch exercises or classes to keep workouts exciting.
- Workout with a partner: Social support improves adherence and accountability.
- Track progress visually: Photos, charts, and graphs of weight lifted or body measurements reinforce improvement.
Data Insight: Studies show that tracking workouts and progress can increase adherence to fitness programs by up to 40%.
3. Using Tracking, Challenges, and Rewards
Motivation can be reinforced by gamifying your fitness journey:
- Challenges: Participate in 30-day push-up or squat challenges.
- Reward Systems: Treat yourself to non-food rewards (new gym gear, massage, or a day trip) for hitting milestones.
- Progress Tracking: Maintain a workout log, app, or journal to visualize gains over time.
4. Mental Strategies for Long-Term Success
- Visualization: Picture yourself achieving your gym goers goal, feeling stronger, fitter, and healthier. Visualization primes your brain to take actions consistent with success.
- Affirmations: Positive self-talk such as “I am getting stronger every day” reinforces consistency.
- Routine Building: Make gym time non-negotiable by scheduling it like a work appointment. Habits reduce reliance on motivation alone.
Pro Tip: Motivation fluctuates, but habits and mindset maintain progress. Build routines that last beyond temporary bursts of energy.
5. Featured Snippet Opportunity – Top 5 Ways to Stay Motivated at the Gym
- Set small, achievable micro-goals.
- Track progress visually with photos or charts.
- Change routines to prevent boredom.
- Use social accountability—work out with friends or online groups.
- Reward yourself for consistency and milestones.
Key Takeaways:
- Mindset and motivation are critical pillars for achieving any gym goal.
- A growth mindset, visualization, and habit-building increase long-term success.
- Overcoming slumps requires structured strategies, tracking, and rewards.
Tracking Progress and Adjusting Goals for Gym Goers
Once you’ve set a gym goers goal, created a workout plan, and optimized your nutrition, the next step is tracking your progress. Monitoring results allows you to identify what works, adjust what doesn’t, and ensure long-term success. Without proper tracking, even a solid routine can fail to deliver maximum results.
1. How to Measure Success
Success can be measured in multiple ways depending on your fitness goal:
- Weight Loss Goals:
- Scale weight (weekly, not daily)
- Body fat percentage (using calipers or smart scales)
- Inches lost from waist, hips, and chest
- Muscle Gain Goals:
- Strength increases (weight lifted, number of reps)
- Muscle circumference measurements
- Visual progress via photos
- Endurance/Performance Goals:
- Time to complete a run or workout
- Heart rate recovery
- Number of reps or circuits completed
- Flexibility and Mobility Goals:
- Range of motion measurements
- Ability to perform new movements comfortably
Pro Tip: Combine quantitative (numbers) and qualitative (how you feel) measurements for a holistic view of progress.
2. Using Apps, Journals, or Photos to Track Progress
There are several ways to track your gym progress efficiently:
- Fitness Apps: MyFitnessPal, Strong, or Fitbod allow tracking workouts, nutrition, and body stats.
- Journals: Writing sets, reps, weights, and personal notes helps you spot trends and improvements.
- Photos: Weekly or monthly progress pictures show visual changes that scales can’t capture.
Case Study: A NYT Health article highlighted a group of gym-goers who tracked their workouts with photos and logs. After 12 weeks, those who tracked progress consistently gained 30% more muscle mass than those who did not.
3. When to Adjust Your Goals
Even the best gym plans sometimes require tweaks:
- Plateaus: If fat loss or muscle gain stalls, consider adjusting workout intensity, volume, or nutrition.
- Time Constraints: Modify your plan if life gets busy—shorter, high-intensity sessions can maintain progress.
- Injury or Recovery Needs: Scale back intensity or focus on alternative exercises to avoid setbacks.
Guideline: Reassess your gym goers goal every 4–6 weeks to ensure it remains realistic, challenging, and aligned with your progress.
4. Signs of Overtraining or Stagnation
Overtraining can undermine progress and lead to burnout. Watch for:
- Persistent fatigue or soreness
- Plateauing strength or endurance
- Sleep disturbances
- Increased irritability or lack of motivation
Solution: Incorporate rest days, active recovery, and proper nutrition to allow your body to adapt and grow.
5. Featured Snippet Opportunity – How to Track Gym Progress Effectively
- Define measurable indicators for your specific goal (weight, strength, endurance, flexibility).
- Track weekly using apps, journals, or photos.
- Review progress every 4–6 weeks.
- Adjust workouts, nutrition, or intensity if results plateau.
- Include rest and recovery to prevent overtraining.
Key Takeaways:
- Consistent tracking ensures your gym goers goal stays on course.
- Adjust your plan based on real data and feedback from your body.
- Combining numbers, visual evidence, and how you feel provides the clearest picture of progress.
Common Challenges Gym Goers Face and How to Overcome Them
Even the most dedicated individuals face hurdles when pursuing a gym goers goal. Identifying these challenges early and having strategies to overcome them can prevent plateaus, injuries, and burnout, keeping your fitness journey on track.
1. Plateaus in Weight Loss or Muscle Gain
A plateau happens when your body adapts to your routine and progress slows down. This is one of the most common frustrations for gym-goers.
How to Overcome:
- Change your workout routine: Swap exercises, increase intensity, or try new training methods (e.g., supersets or circuits).
- Reassess nutrition: Ensure your calorie intake aligns with your current goal—sometimes fat loss stalls due to underestimated calories, or muscle gain stalls due to insufficient protein.
- Incorporate rest: Overtraining can cause stagnation; adding recovery days allows muscles to grow and metabolism to regulate.
Tip: Tracking workouts and nutrition helps identify exactly where progress stalls.
2. Time Management and Scheduling Conflicts
Many gym-goers struggle to fit workouts into busy lives, leading to skipped sessions or inconsistent training.
Strategies to Overcome:
- Plan workouts in advance: Schedule sessions like appointments to reduce the chance of skipping them.
- Opt for shorter, high-intensity sessions: Even 20–30 minutes of HIIT or circuit training can be effective.
- Prioritize consistency over duration: It’s better to work out regularly for shorter periods than infrequently for long sessions.
Pro Tip: Early morning workouts reduce distractions and increase adherence for busy schedules.
3. Avoiding Injuries and Burnout
Injuries or burnout can derail a gym goers goal and affect motivation. Common causes include poor form, lifting too heavy, or inadequate recovery.
How to Prevent Injuries:
- Warm-up and stretch before every workout.
- Focus on proper technique over heavy weights.
- Listen to your body—pain is a warning, not a badge of effort.
- Include mobility and recovery sessions in your routine.
Burnout Prevention: Rotate workouts, include rest days, and keep variety in exercises to maintain interest and motivation.
4. Maintaining Consistency Long-Term
Consistency is the ultimate factor in achieving any gym goers goal. Even a perfect plan fails if it isn’t followed consistently.
Strategies to Stay Consistent:
- Track progress: Visual cues like charts, apps, or progress photos maintain motivation.
- Set realistic expectations: Avoid setting goals that are impossible to maintain; small, steady progress wins long-term.
- Reward yourself: Non-food rewards for milestones reinforce behavior and make the process enjoyable.
- Find support: Training partners, online communities, or personal trainers provide accountability and encouragement.
Data Insight: Research from NYT Health shows that individuals who maintained consistent gym attendance for 6 months experienced 60% greater improvements in strength and body composition compared to inconsistent gym-goers.
5. Featured Snippet Opportunity – 4 Common Challenges and Solutions
- Plateaus: Change routine, adjust nutrition, or add recovery days.
- Time Constraints: Plan workouts, prioritize short high-intensity sessions.
- Injuries/Burnout: Warm-up, proper form, mobility, and rest days.
- Consistency: Track progress, set realistic goals, and find social support.
Key Takeaways:
- Recognizing and preparing for common gym challenges keeps your gym goers goal achievable.
- Regularly reassessing workouts, nutrition, and recovery prevents stagnation and injuries.
- Building a strong support system and maintaining consistency are critical for long-term success.
Success Stories and Case Studies of Gym Goers
Hearing real-life success stories can inspire and guide gym-goers to achieve their own fitness goals. Whether it’s weight loss, muscle gain, or endurance improvement, learning from others’ experiences provides actionable lessons and motivation.
1. Weight Loss Transformation
Case Study: Sarah, 32, from New York
- Goal: Lose 20 lbs and reduce body fat from 28% to 18% in 6 months
- Strategy: Sarah combined HIIT workouts 4 times a week with strength training 2 times a week. She followed a high-protein, moderate-carb diet and tracked her meals using an app.
- Result: Sarah achieved her goal in 5 months, reporting increased energy, better sleep, and improved self-confidence.
Lessons Learned:
- Consistent tracking of both workouts and nutrition is key.
- Mixing cardio with strength training preserves muscle while promoting fat loss.
- Setting intermediate goals (5 lbs per month) keeps motivation high.
2. Muscle Gain and Strength Improvement
Case Study: James, 28, from Boston
- Goal: Increase lean muscle mass and improve overall strength
- Strategy: Focused on progressive overload with a 5-day resistance training program. He ate a calorie surplus diet rich in protein (2 g/kg body weight/day) and incorporated recovery days for muscle repair.
- Result: In 6 months, James gained 6 kg of lean muscle and increased his bench press from 80 kg to 110 kg.
Lessons Learned:
- Structured routines with compound exercises accelerate muscle growth.
- Recovery and sleep are just as important as training intensity.
- Tracking strength gains weekly helps identify plateaus early.
3. Endurance and Performance Improvement
Case Study: Aisha, 25, from Chicago
- Goal: Complete her first half-marathon and improve overall cardiovascular endurance
- Strategy: Aisha followed a progressive running schedule, combined with cycling and swimming for cross-training. She also incorporated mobility and flexibility exercises to prevent injury.
- Result: Successfully completed her half-marathon in 2 hours, improved her VO2 max by 15%, and reduced recovery time after intense training sessions.
Lessons Learned:
- Gradual progression prevents injuries and builds confidence.
- Cross-training improves endurance while reducing the risk of overuse injuries.
- Tracking performance metrics like pace, distance, and heart rate optimizes results.
4. Flexibility and Mobility Success
Case Study: Michael, 40, from San Francisco
- Goal: Improve shoulder mobility and prevent chronic lower back pain
- Strategy: Michael incorporated daily yoga, mobility drills, and foam rolling, along with core strengthening exercises.
- Result: After 12 weeks, he reported full shoulder mobility, reduced back discomfort, and enhanced overall functional fitness.
Lessons Learned:
- Small daily investments in mobility lead to significant improvements over time.
- Combining mobility with strength exercises creates a balanced and sustainable fitness routine.
- Tracking range of motion progress ensures measurable improvement.
5. Key Takeaways from Success Stories
- Consistency is the common thread in all success stories. Whether for weight loss, muscle gain, or endurance, regular effort yields results.
- Tracking and adjusting workouts and nutrition is essential for overcoming plateaus.
- Recovery and mindset are equally important as physical training.
- Setting SMART goals and breaking them into short-term milestones increases the likelihood of success.
- Inspiration from real-life examples demonstrates that any gym-goers goal is achievable with a structured approach.
Frequently Asked Questions About Gym Goers Goal
1. How long does it take to achieve a gym goal?
The timeline depends on the type of goal:
- Weight Loss: Safe and sustainable fat loss is 0.5–1 kg per week. A 10–kg loss may take 10–20 weeks.
- Muscle Gain: Beginners can expect 1–2 kg of lean muscle per month with proper training and nutrition. Advanced lifters progress slower.
- Endurance or Performance Goals: Improvements can be seen in 4–8 weeks, but achieving peak endurance may take several months.
Tip: Consistency and tracking are more important than speed. Rapid results often lead to burnout or injuries.
2. Should I focus more on diet or exercise?
Both are essential, but nutrition usually has a larger impact on results:
- For weight loss, diet accounts for ~70–80% of progress.
- For muscle gain, protein intake and calorie surplus are crucial alongside strength training.
- Performance and endurance require a balance of both, including proper timing of meals.
Pro Tip: Track both workouts and food intake to ensure balanced progress.
3. How many days a week should I work out?
- Beginners: 3–4 days per week focusing on full-body workouts.
- Intermediate: 4–5 days per week with split routines (e.g., upper/lower body).
- Advanced: 5–6 days per week with targeted workouts for specific goals.
Tip: Rest and recovery days are as important as active workout days to prevent injuries and promote growth.
4. Can beginners achieve the same results as advanced gym-goers?
Yes, but expectations should be realistic:
- Beginners often see faster initial progress due to “newbie gains.”
- Advanced gym-goers require more structured routines and incremental adjustments for continued improvement.
- Individual genetics, lifestyle, and consistency affect results.
5. Is it better to follow a personal trainer or an online plan?
- Personal Trainer: Offers customized guidance, real-time corrections, and accountability. Ideal for beginners or those with specific goals.
- Online Plans: Convenient, affordable, and flexible. Works well if you are self-motivated and have some experience.
Pro Tip: Many gym-goers start with a personal trainer to learn proper form, then transition to a structured online plan for long-term sustainability.
6. Featured Snippet Opportunity – Quick FAQ Summary
Top 5 Quick Answers:
- Timeline: 4–20 weeks depending on your goal.
- Diet vs Exercise: Diet often has a greater impact on results.
- Workout Frequency: 3–6 days/week based on experience level.
- Beginners vs Advanced: Beginners see faster initial gains; advanced require structured progression.
- Trainer vs Online Plan: Trainers provide guidance; online plans work if you’re self-motivated.
Key Takeaways:
- FAQs address the most common doubts about gym goers goal, providing clarity and actionable advice.
- Proper expectations, combined with consistent tracking and structured routines, dramatically increase chances of success.
- Structuring content in Q&A format improves user experience and SEO by targeting featured snippet opportunities.
Conclusion: Achieving Your Gym Goers Goal
Achieving a gym goers goal (perhaps NYT) requires a combination of strategy, consistency, and mindset. From setting clear SMART goals, following tailored workout plans, optimizing nutrition, staying motivated, and tracking progress, every step plays a crucial role in your success.
Key takeaways from this guide include:
- Define Your Goal Clearly: Whether it’s weight loss, muscle gain, endurance, or flexibility, understanding your objective guides all decisions.
- Create a Structured Plan: Workouts should align with your goal, incorporating a balance of strength, cardio, and mobility.
- Fuel Your Body Properly: Nutrition is the foundation of progress. Balance macronutrients, time meals around workouts, stay hydrated, and supplement smartly.
- Build a Strong Mindset: Motivation fluctuates, but habits, visualization, and tracking maintain consistency.
- Track and Adjust: Use apps, journals, and progress photos to monitor results, and tweak your plan to overcome plateaus or challenges.
- Overcome Challenges: Be prepared for plateaus, injuries, time constraints, and motivational dips, and develop strategies to address them.
Final Advice: Start small, stay consistent, and track every step of your journey. Even minor, steady progress compounds over time, leading to remarkable transformations. Remember, success is not just about hitting the gym—it’s about creating a sustainable, goal-oriented lifestyle.
Call-to-Action: Take a moment today to write down your gym goers goal, plan your workouts and nutrition, and commit to tracking your progress. Every step forward, no matter how small, brings you closer to your fitness aspirations.